In today’s digital era, cloud adoption has become a strategic imperative for companies of all sizes and kinds. We can say that no industry is an exception; the ability to scale quickly, innovate and respond to market demands is crucial. Cloud services platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offer a robust set of services and tools that enable enterprises to transform their operations and gain competitive advantage.
However, with the great power and flexibility that these cloud services offer, also come significant challenges in terms of management and cost optimization. Pricing structures can be complex and costs can escalate quickly if not managed effectively. This is where cloud cost optimization comes into play: a critical discipline that seeks to balance performance and price paid, ensuring that cloud resources are used as efficiently as possible.
Although there are many cloud providers in the market, the dominant ones are AWS, Azure and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). AWS began by offering a wide variety of services and a consumption-based pricing structure. This is an approach that other providers have followed and means that you pay for what you use, but it also means that costs can escalate quickly if not managed properly. Azure is known for its integration with other Microsoft products and for offering discounts for companies already working in the Microsoft ecosystem. GCP, on the other hand, with its strong focus on data analytics and machine learning, also offers competitive pricing and innovative solutions.
Cost management in cloud can be a complex task that requires a clear understanding of pricing models, constant monitoring of resource usage and implementation of optimization practices and strategies. This is where FinOps (Cloud Financial Operations) plays a crucial role. FinOps is an emerging practice that seeks to bring financial agility and efficiency to the variable and dynamic nature of cloud spending. It involves close collaboration between finance, operations and development teams to ensure that every euro spent in the cloud is used in the most effective way possible.
But being cost conscious is not just an issue for FinOps. Adopting a culture of cost accountability in the enterprise is vital. This involves creating an environment where everyone involved, from developers to managers to finance teams, is aware of what is being paid for cloud resources and is committed to optimizing these resources. It’s about changing the mindset from “just run it in the cloud” to “run it efficiently in the cloud.”
And we must remember that the dynamic and complex nature of the cloud can make cost management a challenge.
Pricing models
While all cloud providers are essentially pay-as-you-go, each has its own pricing model, and the primary key to optimizing costs on any platform is a thorough understanding of their pricing models and implementing resource management practices. This includes choosing resource types and making appropriate use of them, implementing autoscaling to match resources to real-time demand, and continuously monitoring and adjusting usage to make sure you’re not paying for resources you don’t need.
To help us do this, providers often offer estimation tools and monitors that will allow us to adjust the services used to improve our costs and performance.
- AWS Pricing: https://aws.amazon.com/pricing/
- Azure Pricing: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/pricing/
- Google Cloud Pricing: https://cloud.google.com/pricing
In addition, in all major providers, it is possible to set quotas and alarms when reaching certain levels of expending, to avoid major scares at the time of receiving the bill. Making use of them is highly recommended, both at a personal level and at a business level.
Cost Optimization Strategies
Once you have a solid understanding of the pricing models of different cloud service providers, you can implement effective cost optimization strategies. These strategies will maximize performance while minimizing expenses. Without going into detail (I recommend going to each particular provider), some of the strategies we can follow are:
Reservations and Long-Term Commitments.
By purchasing reserved instances, you can get a significant discount compared to normal on-demand instance rates. This option is ideal for workloads with predictable capacity needs.
Use of Spot or Interruptible Instances
Spot or interruptible instances allow users to bid for unused capacity at significantly reduced prices. However, these instances can be terminated by suppliers at short notice if the capacity is needed. Depending on the provider, they may appear as spot, interruptible or preemptible.
These types of instances are ideal for batch jobs.
Auto Scaling and Resource Management
All providers offer auto-scaling capabilities that allow you to automatically adjust resources to meet demand, ensuring you only pay for what you need.
Elimination of Unused or Underutilized Resources
Use third-party tools such as CloudHealth, Dynatrace or Apptio Cloudability among many others to identify and eliminate unused or underutilized resources.
Storage Optimization
AWS, Azure and GCP offer various classes of storage, allowing you to move less accessed data to lower cost storage (although it takes longer to retrieve information).
Automation and Scripting
- Automations: Most vendors offer configurations and automations to shut down resources at certain times or under certain circumstances.
- Custom Scripts: Implement scripts to automatically shut down resources during non-working hours or when they are not needed.
Monitoring and Alerts
Use of monitoring tools such as AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor and GCP monitoring tools to set alerts and track resource usage.
Cost Management Tools and Services
As companies expand their cloud operations, cost management becomes an increasingly important and complex task. Fortunately, there are numerous tools and services designed specifically to help organizations monitor, analyze and optimize their cloud expenses.
Every major cloud service provider offers integrated cost management tools, for example:
In addition to native tools, there are third-party solutions that offer advanced functionalities and support for multiple platforms. Some examples are CloudHealth by VMware or Apptio Cloudability, although there are many others.
To know which tool is best suited to our needs, we can base ourselves on aspects such as:
- Integration: Ensure that the tool integrates easily with existing infrastructure and services.
- Scalability: The solution must be able to handle the growth of cloud operations.
- Functionality: Depending on the needs, advanced features such as predictive analytics, optimization recommendations or support for custom policies may be desired.
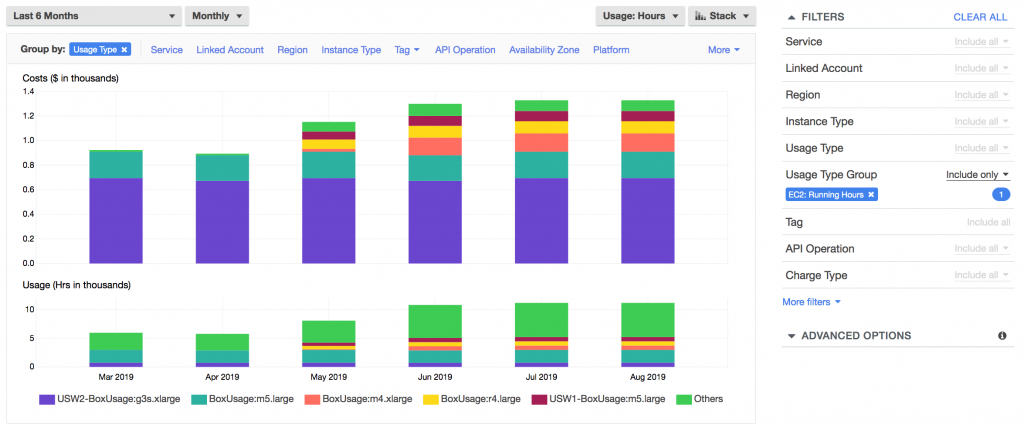
Beyond the tools and as we will see below, it is crucial to adopt a culture where each team understands and is accountable for its spending. To do so, we can use:
- Regular Cost Reports: Setting up routines to review and discuss expenses in the cloud, making sure all teams are aware of their expenses.
- Automatic Alerts: Setting up alerts to notify teams when expenses exceed established budgets or when anomalies arise.
FinOps
If we talk about cloud costs, we can’t forget FinOps. Financial management of cloud operations, known as FinOps, is an essential practice for companies looking to optimize their cloud spending and ensure efficient use of resources. FinOps combines systems, best practices and culture to increase enterprise agility and provide greater visibility and control over cloud spending.
We can summarize the basic principles of FinOps as:
- Collaboration: Teams work together to understand and manage cloud usage and cost.
- Accountability: Each team has clear responsibility for managing resources and costs.
- Transparency: Full visibility into costs and usage to make informed decisions.
By implementing FinOps principles and practices, companies can foster a culture of accountability, transparency and continuous optimization, leading to greater agility and financial performance.
In practice, it involves close collaboration between finance, operations and development teams to understand spend, make informed decisions and ensure optimal performance without waste of resources.
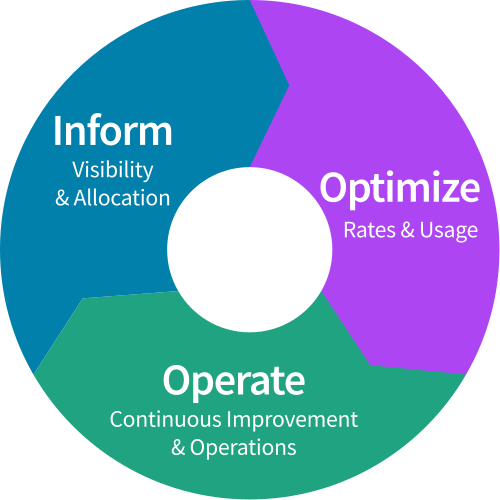
Implementing FinOps requires a cultural shift, where everyone involved understands their role in managing costs in the cloud. It is a change in mindset and the way of working in aspects such as:
- Education and Training: Teams need to understand cloud cost structures and how their actions impact spend.
- Tools and Automation: Use cost management and automation tools to provide visibility and control.
- Metrics and KPIs: Establish key performance indicators to measure and optimize usage and costs.
Cost Accountability Environment
We have already seen that establishing a cost accountability environment is critical to maximizing efficiency and minimizing unnecessary expenses in the cloud infrastructure. But this approach involves not only implementing the right tools and processes, but also fostering an organizational culture that promotes transparency and accountability for costs incurred.
Creating this environment of accountability starts with organizational culture. It is crucial that everyone in the organization, from developers to executives, understands the importance of cost management and takes responsibility for the resources they use. Education and awareness play a crucial role, so it is important to conduct training sessions to ensure that all employees understand the costs associated with resources and how they can contribute to their optimization.
Defining clear policies regarding the use of cloud resources, including budget allocation and accountability for overages, will avoid misunderstandings and provide a higher level of accountability. On the other hand, the use of key performance indicators (KPIs), analysis and regular reporting will help us to extend the culture of cost accountability.
Organizations that invest in the knowledge, tools and culture to manage their cloud spend will not only achieve significant savings, but also position their teams for innovation and long-term success.