Data-driven world companies rely heavily on the seamless flow of information to maintain efficiency, make informed decisions, and stay competitive. Data flows have become the lifeblood of modern enterprises.
Data flows represent the movement of data between organizations, different parts of an organization, countries, systems, or processes. Understanding and optimizing these flows is crucial for any enterprise aiming to leverage data effectively. These flows of information across borders and systems are key for businesses of all sizes to operate efficiently, innovate, and compete on a global scale.
Data flows refer to the movement of digital information and this includes everything from customer data and financial transactions to operational metrics and market research. In essence, data flows encompass any digital information that moves from one point to another.
These pathways can be visualized using Data Flow Diagrams (DFD) and matrices, which illustrate how data moves from one process to another, where it is stored, and how it is accessed. DFDs help in understanding the structure and flow of data, making it easier its integration and interoperability.
In short, data flows map and document relationships between data and:
- Applications within a business process
- Data stores or databases in an environment
- Network segments (useful for security mapping)
- Business roles, depicting which roles have responsibility for creating, updating, using, and deleting data (CRUD)
- Locations
What are they like?
Data flows can be documented at different levels of detail for example subject Area, business entity, or even the attribute level.
Data flows can be represented in many ways but the most used ones are using two-dimensional matrices (we can also perform the mapping using capabilities instead of business processes).
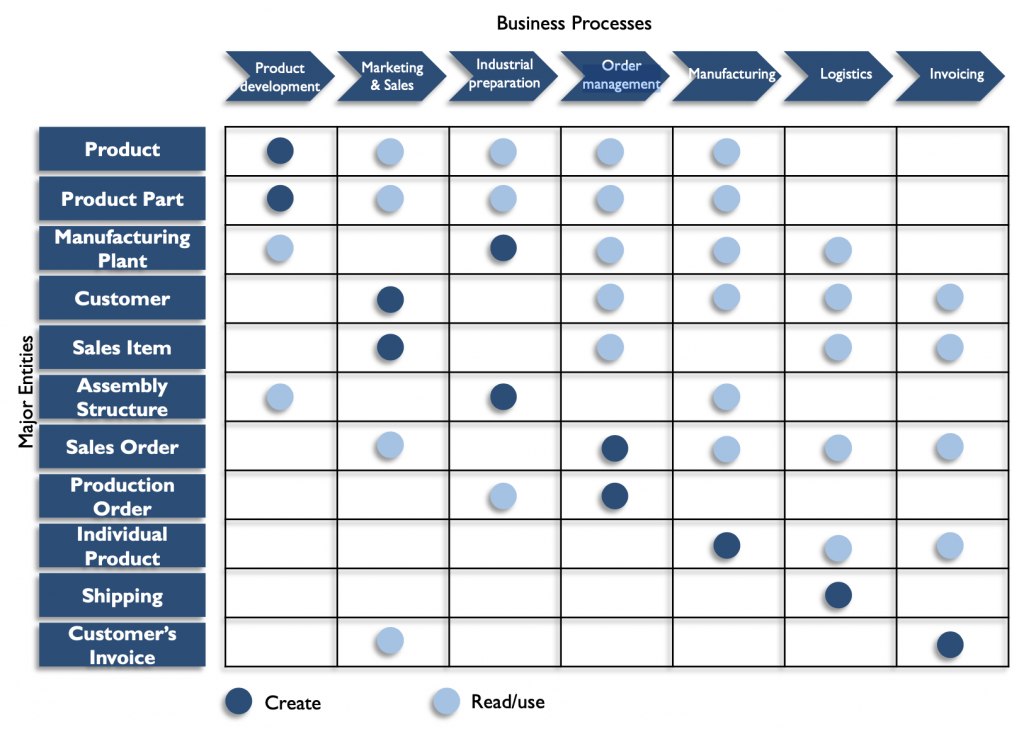
And in data flow diagrams. To represent data flow diagrams we have various nomenclatures. The most commonly used are:
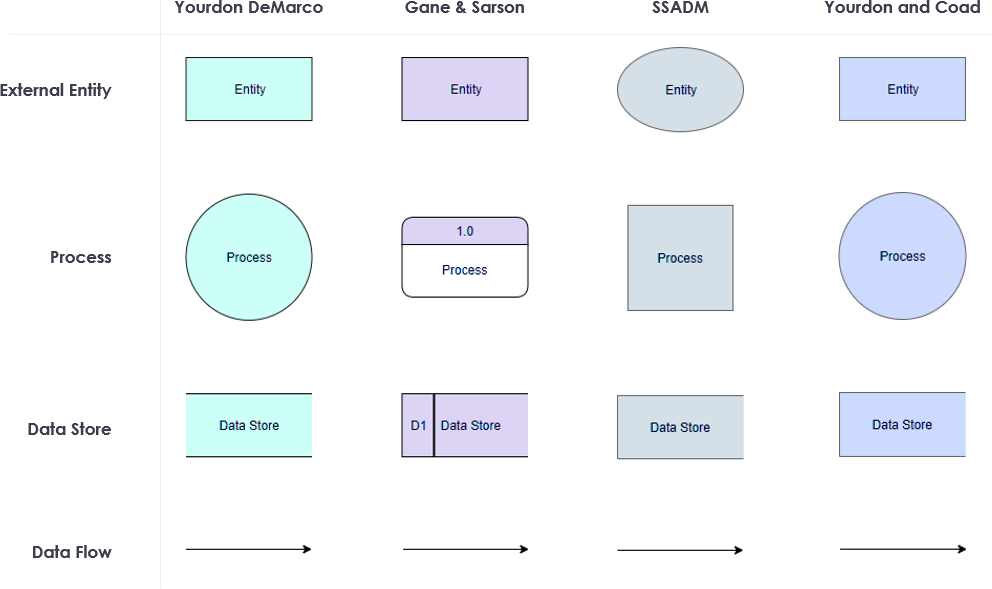
Challenges and Considerations
While data flows offer numerous benefits, enterprises must also navigate several challenges:
- Data Privacy and Security: As data moves across borders and systems, ensuring its privacy and security becomes increasingly complex. Enterprises must implement robust security measures and comply with various data protection regulations like GDPR.
- Data Governance: Effective data governance is crucial for maintaining data quality, consistency, and compliance across the organization. This includes establishing clear policies for data collection, storage, and usage.
- Technical Infrastructure: To support efficient data flows, enterprises need to invest in scalable and interoperable technical infrastructure. This may involve cloud computing, edge processing, and advanced networking technologies.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the complex landscape of international data regulations can be challenging. Enterprises must stay informed about data localization requirements, cross-border transfer restrictions, and other regulatory issues.
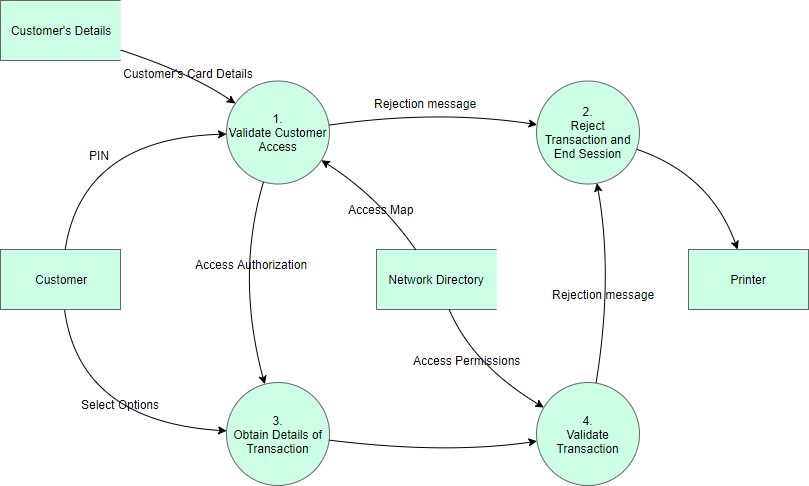
How to create a data flow
As a simple guide on how to create a data flow, let’s help this boy with his lemonade stand. He will sell lemonade to some customers, but first he has to buy the lemons from his supplier. He will also pay his sister who helps him in the stand.

Step 1: Identify Major Inputs and Outputs
Begin by identifying the key inputs and outputs of your system. Inputs are the data that enters the system from external sources, while outputs are the data that leaves the system to external destinations.
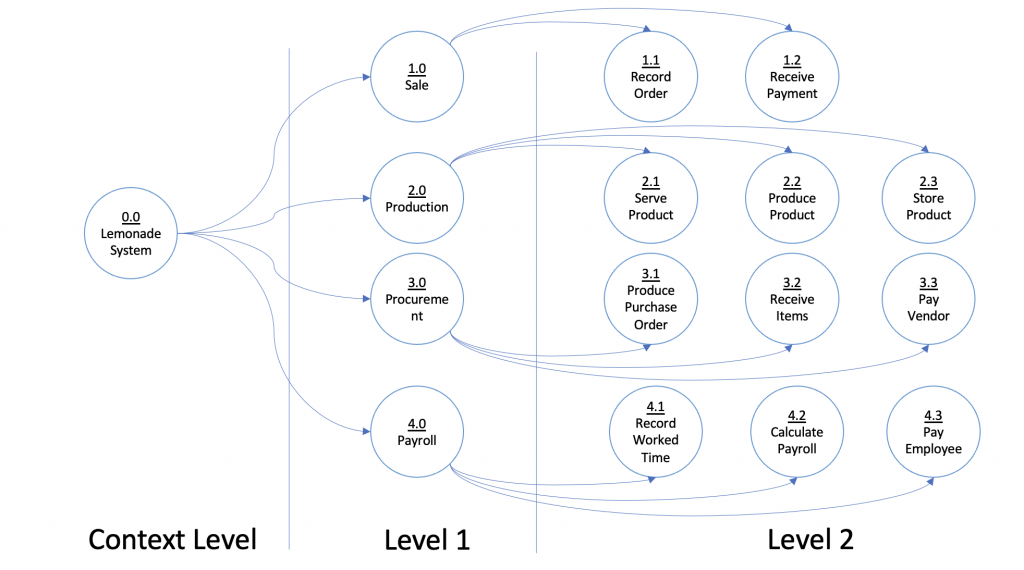
Step 2: Build a Context Diagram
A context diagram is a high-level, simplified view of your system that shows the system as a single process and its interactions with external entities. This helps in understanding the scope of the system and its boundaries. It shows the interactions of the system with the customers, the lemon supplier and his sister (the employee).
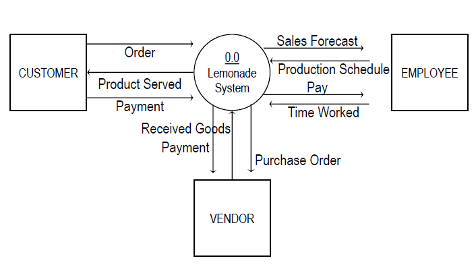
Step 3: Expand the Context Diagram into a Level 1 DFD
Next, break down the single process in your context diagram into multiple subprocesses. This is known as a Level 1 Data Flow Diagram (DFD). Each subprocess should represent a major function within the system. It shows the relationship of each process with external entities.
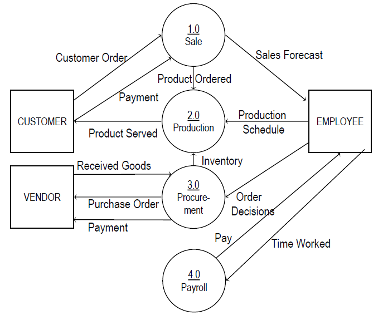
Step 4: Expand to Level 2+ DFDs
For more detailed analysis, you can further decompose each subprocess into smaller processes, creating Level 2 or higher DFDs. This helps in understanding the finer details of data movement and storage within the system.
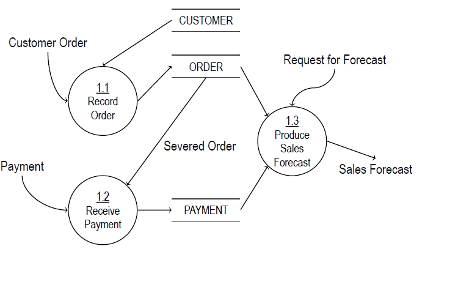
Step 5: Confirm the Accuracy of Your Final Diagram
Review your diagrams to ensure they accurately represent the data flows within your system. Validate them with stakeholders to confirm that all processes, data stores, and data flows are correctly depicted.
Why are data flows important?
There are many reasons why it is in a company’s interest to have complete and up-to-date data flows. Apart from the typical reasons such as show how data is shared and used across the organization, identify data lineage from / to systems and applications or assist root cause analysis of issues, data flows are important also to:
- Enhance Operational Efficiency: By understanding data flows, organizations can streamline processes, reduce redundancies, and eliminate bottlenecks. For instance, providing seamless communication between different departments and offices.
- Enhance Decision-Making: Data flows enable enterprises to gather and analyze data from various sources, providing a comprehensive view of the business. This holistic perspective is essential for making informed decisions that drive growth and efficiency.
- Improve Data Quality: Properly managed data flows ensure that data is accurate, consistent, and up-to-date. This is critical for maintaining data integrity and reliability, which are essential for analytics and reporting
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries are subject to strict data regulations. Understanding data flows helps enterprises ensure compliance with these regulations by tracking data movement and access
- Enhance Collaboration: Data flows facilitate better communication and collaboration between different departments. When data moves seamlessly across the organization, teams can work together more effectively, leading to improved outcomes
- Driving Innovation and Growth: Data flows are essential for fostering innovation and driving business growth. By allowing information to move freely, companies can, for example, analyze market trends and consumer behavior across different regions
- Facilitating Expansion: For enterprises looking to expand and integrate with other business, data flows are indispensable. For instance, they allow companies to comply with various regulatory requirements across jurisdictions
- Improving Customer Experience: Data flows play a crucial role in enhancing customer experience by enabling personalized content and recommendations across multiple channels, devices and platforms. Seamless user experience.
Data flows are the backbone of any enterprise’s data strategy. By understanding and optimizing these flows, organizations can enhance decision-making, improve operational efficiency, ensure data quality, and maintain regulatory compliance. Investing in the right tools and practices for managing data flows is essential for any enterprise looking to thrive in the digital age.
In conclusion, data flows are not just important but essential for modern enterprises. They fuel innovation, drive efficiency, and enable global operations. As the digital economy continues to evolve, businesses that can effectively harness and manage their data flows will be best positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape. By understanding the importance of data flows and addressing the associated challenges, enterprises can unlock new opportunities and drive sustainable growth in the digital age.
I didn’t use to take into account data movements until in a project we found sensitive data scattered all over the data flow, but the problem is that we were not clear about the flow itself, so it was very difficult to trace where this uncontrolled information could be